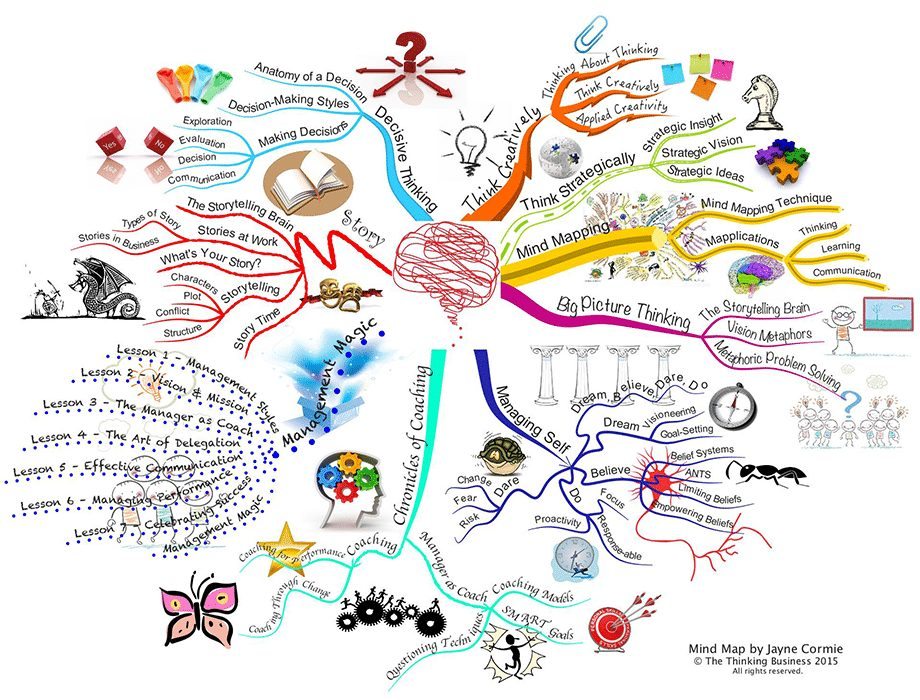
- How To Think Assertivelydialectical Behavioral Training Programs
- Dialectical Behavior Skills
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Certification
- How To Think Assertivelydialectical Behavioral Training Techniques
Previously I have talked about 'Training, What Does It Really Do To The Employee And The Company?', now I will go into some details about Behavioral Training:
This is a free online workbook designed to help people learn cognitive behavioral therapy skills and exercises. CBT has been found in numerous scientific studies to be the most effective treatment for depression, anxiety, and other psychological problems. They keep thinking about those thoughts, and it's all that repetition that seals it in the back of their head. Now their head says, This is an easy thing, I know this one, and it pulls the. Behavioral interview questions are questions that focus on how you've handled different work situations in the past to reveal your personality, abilities and skills. These questions give an interviewer an idea of how you would behave if a similar situation were to arise, the logic being that your success in the past will show success in the future. New Year: New Thinking. Mr S Sneyd, Psychoanalytic Psychotherapist. With the New Year under way, it is time reflect on how you think and feel about yourself, others and life. Don't Tell Me To Stop Training! Mr M Milch, Psychoanalyst. Activity addictions may not put us at mortal risk. Still, like any addictive relationship our dream.
Let me begin with defining behavior:
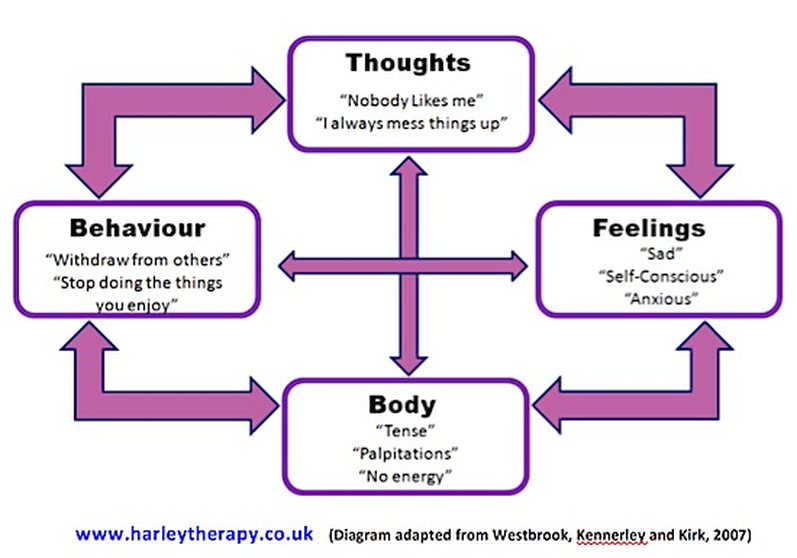
Behavior or behaviouris the range of actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with their environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment. It is the response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary.

Soft skills is a sociological term relating to a person's 'EQ' (Emotional Intelligence Quotient), the cluster of personality traits, social graces, communication, language, personal habits, friendliness, and optimism that characterize relationships with other people. Soft skills complement hard skills which are the occupational requirements of a job and many other activities. Soft skills are personal attributes that enhance an individual's interactions, job performance and career prospects. Unlike hard skills, which are about a person's skill set and ability to perform a certain type of task or activity, soft skills relate to a person's ability to interact effectively with coworkers and customers and are broadly applicable both in and outside the workplace. It has been suggested that in a number of professions, soft skills may be more important over the long-term than occupational skills. The legal profession is one example where the ability to deal with people effectively and politely, more than their mere occupational skills, can determine the professional success of a lawyer. Soft Skills are behavioral competencies. Also known as Interpersonal Skills, or people skills.
According to Wiki.Answers.com; 'Soft skills are skills which are difficult to assign an objective numeric measurement to, such as empathy, or 'being a people person'. Soft skills are a sociological term which refers to the cluster of personality traits, social graces, ability with language, personal habits, friendliness, and optimism that mark people to varying degrees. Soft skills complement hard skills, which are the technical requirements of a job. '
Now that we have defined them, let see the difference between them:

In all the frenzy of training corporate specific topics, people might lose the understanding between soft skills and be behavioral skills
- Soft Skills:
A skill is a behavior or ability a person develops through training or experience, and while all personal skills are behaviors, not all behaviors are skills. For example, telling a joke is a skill; laughing at a joke is a behavior. Some suggest that soft skill stands for the soft communication skills, are skills that does involve enhancement of your capacity as an individual on certain aspects of your work.
- Behavioral Skills:
Behavioral skills deal with how you interact within your own organisation/corporation and with other members of the human resource to include external individuals that involves your organisational/corporation work. Others suggest that behavioral skills are a set of training to develop certain behavioral skill in people, such as how to attend to calls/complaints, front office/reception etc. The process is mechanical and is not designed to influence profound changes in people. It is delivered through demonstration/modeling, instructions, role-play/rehearsal, and feedback.
All in all, I think it is safe to assume that they are both two sides of the same coin, and most companies use only one to describe the two.
Behavioral/Soft skills training examples:
How To Think Assertivelydialectical Behavioral Training Programs
Examples include, but not limited to:
- Communication skills.
- Conflict resolution.
- Negotiation skills.
- Creative problem solving.
- Strategic thinking.
- Team building.
- Influencing skills.
- Time-management skills.
- Interpersonal skills.
- Leadership skills.
Soft skills is a sociological term relating to a person's 'EQ' (Emotional Intelligence Quotient), the cluster of personality traits, social graces, communication, language, personal habits, friendliness, and optimism that characterize relationships with other people. Soft skills complement hard skills which are the occupational requirements of a job and many other activities. Soft skills are personal attributes that enhance an individual's interactions, job performance and career prospects. Unlike hard skills, which are about a person's skill set and ability to perform a certain type of task or activity, soft skills relate to a person's ability to interact effectively with coworkers and customers and are broadly applicable both in and outside the workplace. It has been suggested that in a number of professions, soft skills may be more important over the long-term than occupational skills. The legal profession is one example where the ability to deal with people effectively and politely, more than their mere occupational skills, can determine the professional success of a lawyer. Soft Skills are behavioral competencies. Also known as Interpersonal Skills, or people skills.
According to Wiki.Answers.com; 'Soft skills are skills which are difficult to assign an objective numeric measurement to, such as empathy, or 'being a people person'. Soft skills are a sociological term which refers to the cluster of personality traits, social graces, ability with language, personal habits, friendliness, and optimism that mark people to varying degrees. Soft skills complement hard skills, which are the technical requirements of a job. '
Now that we have defined them, let see the difference between them:
In all the frenzy of training corporate specific topics, people might lose the understanding between soft skills and be behavioral skills
- Soft Skills:
A skill is a behavior or ability a person develops through training or experience, and while all personal skills are behaviors, not all behaviors are skills. For example, telling a joke is a skill; laughing at a joke is a behavior. Some suggest that soft skill stands for the soft communication skills, are skills that does involve enhancement of your capacity as an individual on certain aspects of your work.
- Behavioral Skills:
Behavioral skills deal with how you interact within your own organisation/corporation and with other members of the human resource to include external individuals that involves your organisational/corporation work. Others suggest that behavioral skills are a set of training to develop certain behavioral skill in people, such as how to attend to calls/complaints, front office/reception etc. The process is mechanical and is not designed to influence profound changes in people. It is delivered through demonstration/modeling, instructions, role-play/rehearsal, and feedback.
All in all, I think it is safe to assume that they are both two sides of the same coin, and most companies use only one to describe the two.
Behavioral/Soft skills training examples:
How To Think Assertivelydialectical Behavioral Training Programs
Examples include, but not limited to:
- Communication skills.
- Conflict resolution.
- Negotiation skills.
- Creative problem solving.
- Strategic thinking.
- Team building.
- Influencing skills.
- Time-management skills.
- Interpersonal skills.
- Leadership skills.
Dialectical Behavior Skills
Thinking for a Change 4.0 (T4C) is an integrated cognitive behavioral change program authored by Jack Bush, Ph.D., Barry Glick, Ph.D., and Juliana Taymans, Ph.D., under a cooperative agreement with the National Institute of Corrections (NIC). T4C incorporates research from cognitive restructuring theory, social skills development, and the learning and use of problem solving skills.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Certification
T4C is comprised of 25 lessons that build upon each other, and contains appendices that can be used to craft an aftercare program to meet ongoing cognitive behavioral needs of your group. Not all lessons can be completed in one session, so a typical delivery cycle may take 30 sessions. Sessions should last between one and two hours. Ideally, the curriculum is delivered two times per week, with a minimum recommended dosage of once per week and a maximum of three times per week. Participants must be granted time to complete mandatory homework between each lesson.
The program is designed to be provided to justice-involved adults and youth, males and females. It is intended for groups of eight to twelve and should be delivered only by trained facilitators. Due to its integrated structure, T4C is a closed group, meaning members need to start at the beginning of a cycle, and may not join the group mid-stream (lesson five is a logical cut-off point for new group members).
T4C is provided by corrections professionals in prisons, jails, detention centers, community corrections, probation, and parole settings. The National Institute of Corrections has trained more than 10,000 individuals as T4C group facilitators, and more than 500 trainers who can train additional staff to facilitate the program with justice-involved clients.
How To Think Assertivelydialectical Behavioral Training Techniques
T4C 4.0 represents a significant evolution in the curriculum, both in content and use. It is the most sincere hope of NIC and the authors that the changes enable you and your agency to better serve your clients. Correctional agencies can consider Thinking for a Change as one option in a continuum of interventions to address the cognitive, social, and emotional needs of their client populations.

